---
title: Local API Server
description: Learn how to run Jan's local API server.
[
Jan,
Customizable Intelligence, LLM,
local AI,
privacy focus,
free and open source,
private and offline,
conversational AI,
no-subscription fee,
large language models,
Jan Extensions,
Extensions,
]
---
import { Callout, Steps } from 'nextra/components'
import { Settings, EllipsisVertical } from 'lucide-react'
# Local API Server
Jan includes a built-in API server that is compatible with OpenAI's API specification, allowing you to
interact with AI models through a local HTTP interface. This means you can use Jan as a drop-in replacement
for OpenAI's API, but running entirely on your computer.
Jan uses **llama.cpp** as its core engine for running AI models. If you need a standalone API server without
Jan's desktop interface (for example, in server environments or for command-line usage), you can use it directly
as well after downloading it from [here](https://github.com/ggml-org/llama.cpp).
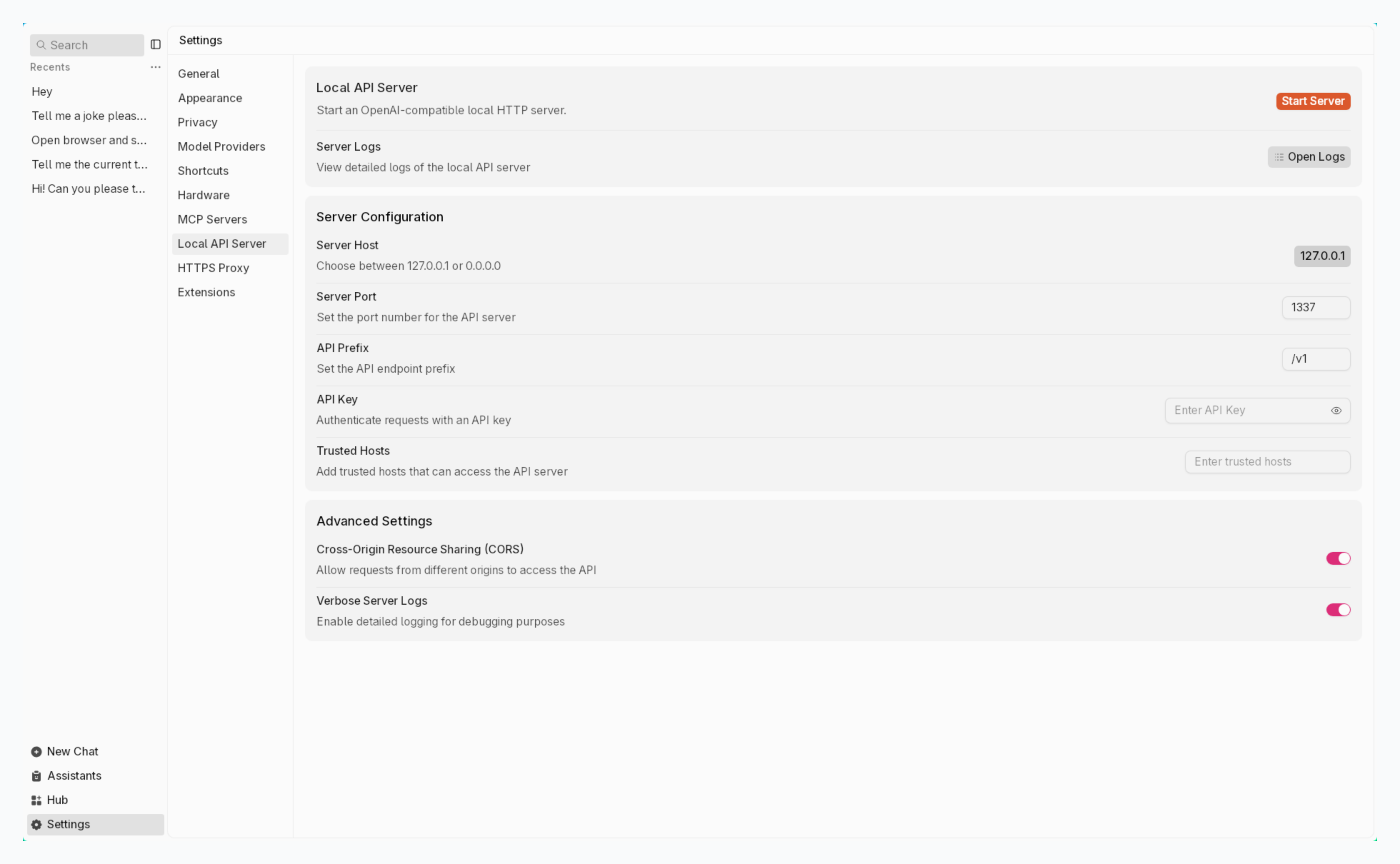
## Start Server
### Step 1: Start Server
1. Navigate to the **Local API Server**
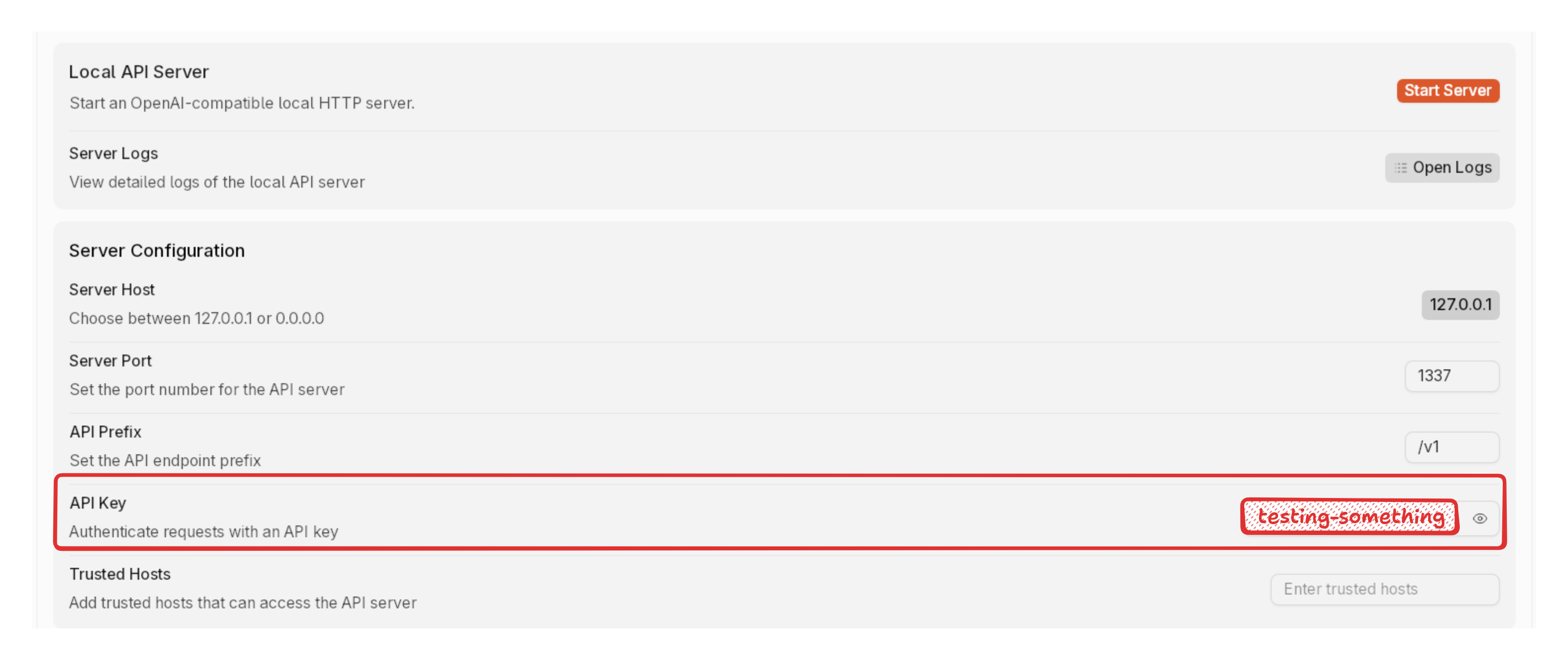
2. Add an API Key (it can be anything) or fully configure the server at [Server Settings](/docs/api-server#server-settings)
3. Click **Start Server** button
4. Wait for the confirmation message in the logs panel, your server is ready when you see: `JAN API listening at: http://127.0.0.1:1337`
5. Make sure you add an API key, this can be anything you want, a word like "testing" or even a combination of numbers and letters.
### Step 2: Test Server
The easiest way to test your server is through the API Playground:
1. Click the **API Playground** button to open its testing interface
2. Select a model from the dropdown menu in Jan interface
3. Try a simple request
4. View the response in real-time
5. When you send requests from another app, you need to add the API key in the request headers.
### Step 3: Use the API
```sh
curl http://127.0.0.1:1337/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer testing-something" \ # here you need to add your API key
-d '{
"model": "jan-nano-gguf",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Write a one-sentence bedtime story about a unicorn."
}
]
}'
```
## Server Settings
#### Host Address Options
- **127.0.0.1 (Recommended)**:
- Only accessible from your computer
- Most secure option for personal use
- **0.0.0.0**:
- Makes server accessible from other devices on your network
- Use with caution and only when necessary
#### Port Number
- Default: `1337`
- Can be any number between 1-65535
- Avoid common ports (80, 443, 3000, 8080) that might be used by other applications
#### API Prefix
- Default: `/v1`
- Defines the base path for all API endpoints
- Example: http://127.0.0.1:1337/v1/chat/completions
#### Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
CORS controls which websites can access your API, which is important for web applications running in browsers.
**When to enable:**
- If you're building a web application that needs to access the API
- If you're using browser extensions
**When to leave disabled:**
- If you're only using the API from your local applications
- If you're concerned about security
#### Verbose Server Logs
Enable to show:
- Detailed information about each API request
- Error messages and debugging information
- Server status updates
## Troubleshooting Guide
Enable **Verbose Server Logs** for detailed error messages.
**1. Common Issues**
- Confirm the server is running
- Check if model is successfully loaded in Jan
- Check if the port is already in use by another application
- Verify you have admin/sudo rights if needed
- Make sure your API endpoint matches your server settings. Example: Using `http://localhost:1337` when you set a different port.
- Make sure the model name in your API request matches exactly what's shown in Jan. Example: If you selected "Llama 3.2 1B Instruct Q8" in Jan, use `llama3.2-1b-instruct` in your API request.
- Verify your JSON request format is correct
- Verify firewall settings
- Look for detailed error messages in the logs
- Make sure you add an API key, this can be anything you want, a word like "testing" or even a combination of numbers and letters.
- Use the API Key in the request headers when sending requests from another app.
**2. CORS Errors in Web Apps**
- Enable CORS in server settings if using from a webpage
- Verify the origin of the request
- Verify your web app's request URL matches the server address exactly
- Check browser console for specific error messages
**3. Performance Issues**
- Monitor system resources (CPU, RAM, and GPU usage)
- Try to reduce the context length or `ngl` (number of GPU layers)
- Check for other resource-intensive applications